
Precipitation
Arizona receives the majority of annual precipitation during two seasons: summer (monsoon season) and winter. Winter precipitation comes from cold fronts and low pressure systems. These systems move south from the Pacific Northwest, often sweeping across Nevada or southern California before bringing cold air and rain or snow into Arizona.
The northern half of the state as well as higher elevations across the state typically receive snowfall in the winter. Northern Arizona receives just over half their annual precipitation in the winter.
The winter storms occasionally extend into southern Arizona. However, southern Arizona receives most of their annual precipitation in the summer. Winter storms rarely bring snow to southern Arizona, but at the highest elevations like Mount Lemmon in Tucson, snow is not uncommon in the winter.
Arizona’s reservoirs largely rely on winter precipitation to refill.
Arizona reservoirs
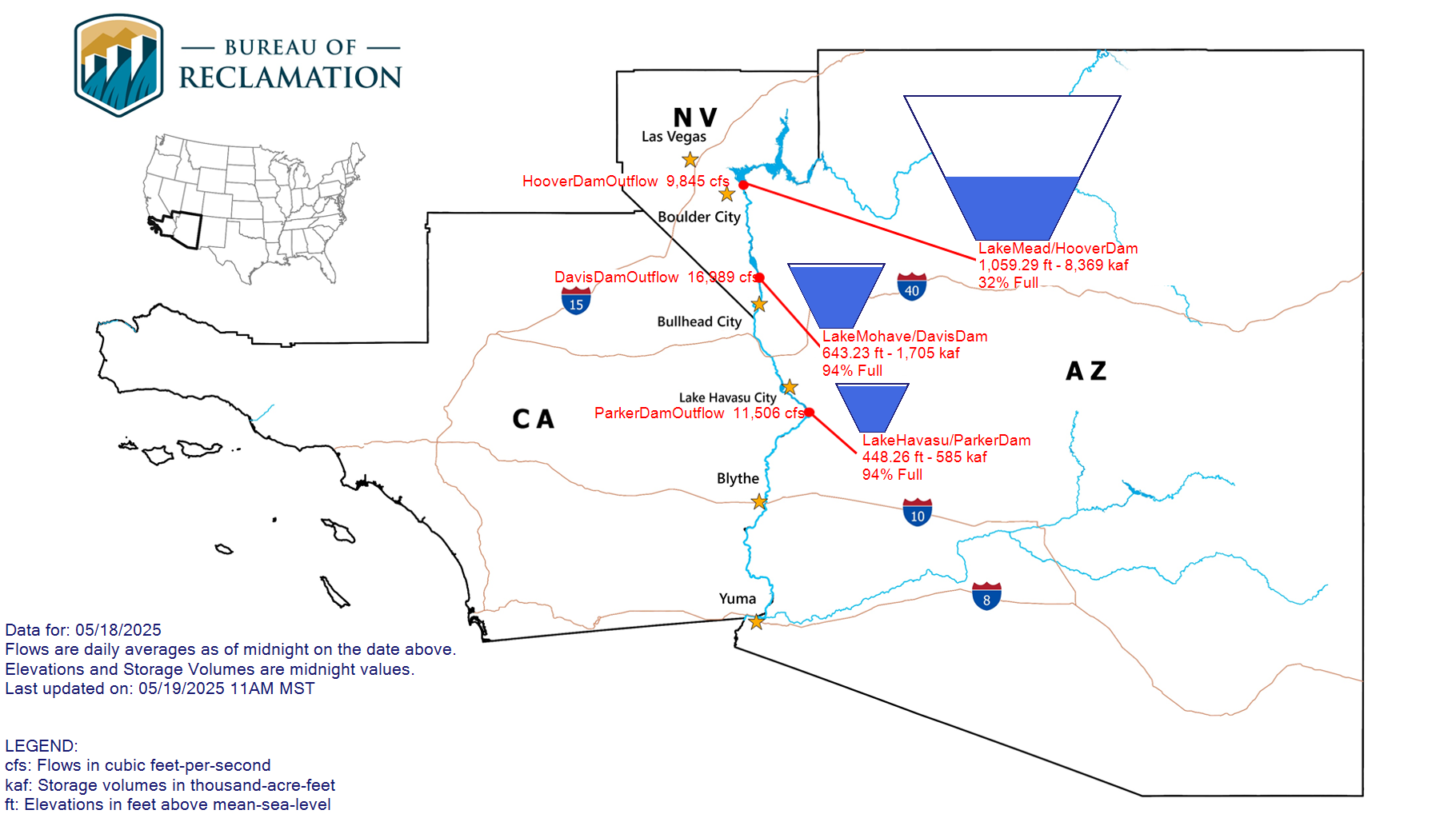
Upper Colorado River Basin Reservoir Levels
Current Colorado River Conditions Dashboard
Salt River Project (SRP) Daily Water Report
Current water levels on Lake Mead and Lake Powell
Precipitation outlooks
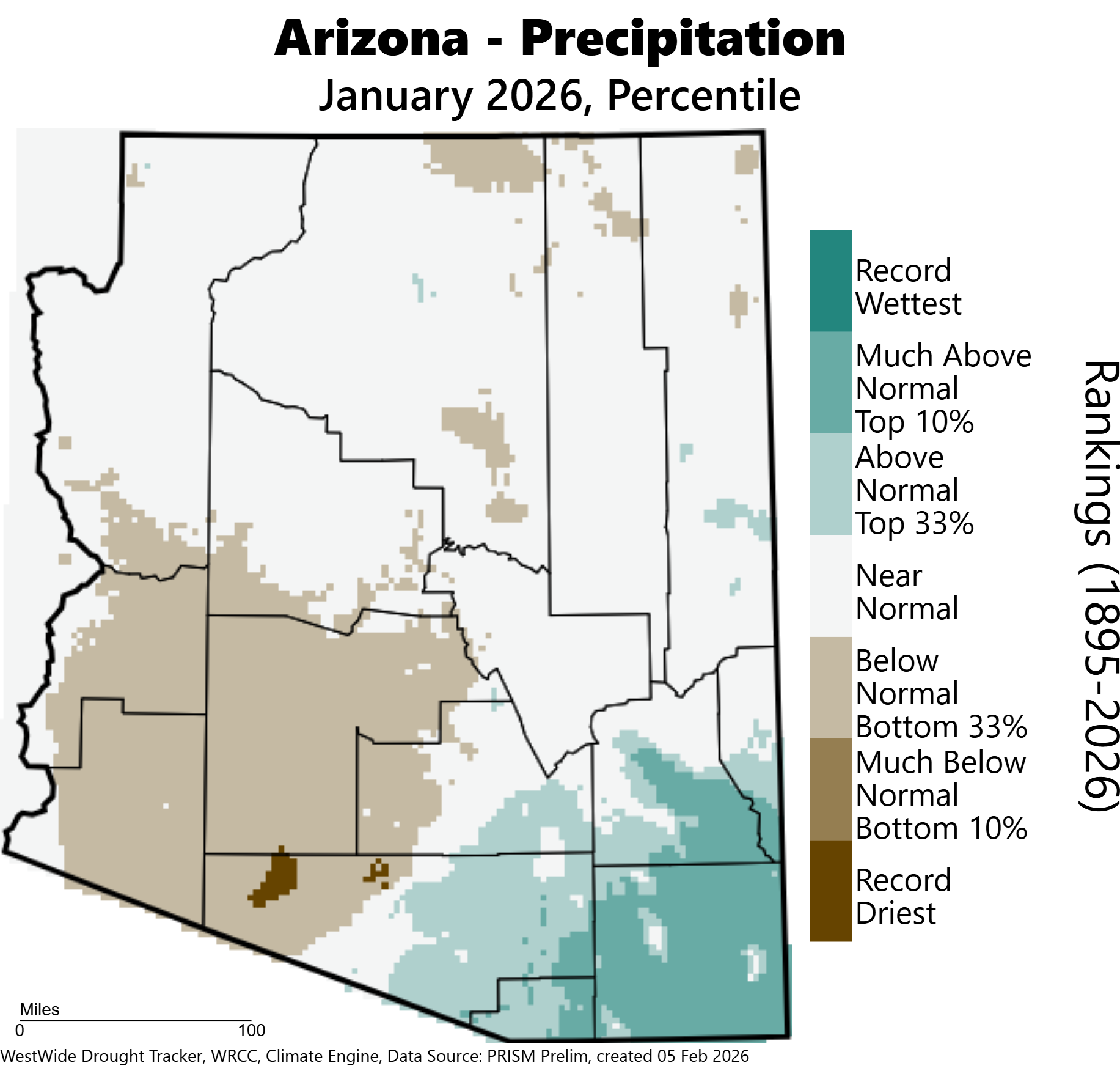
Precipitation ranks
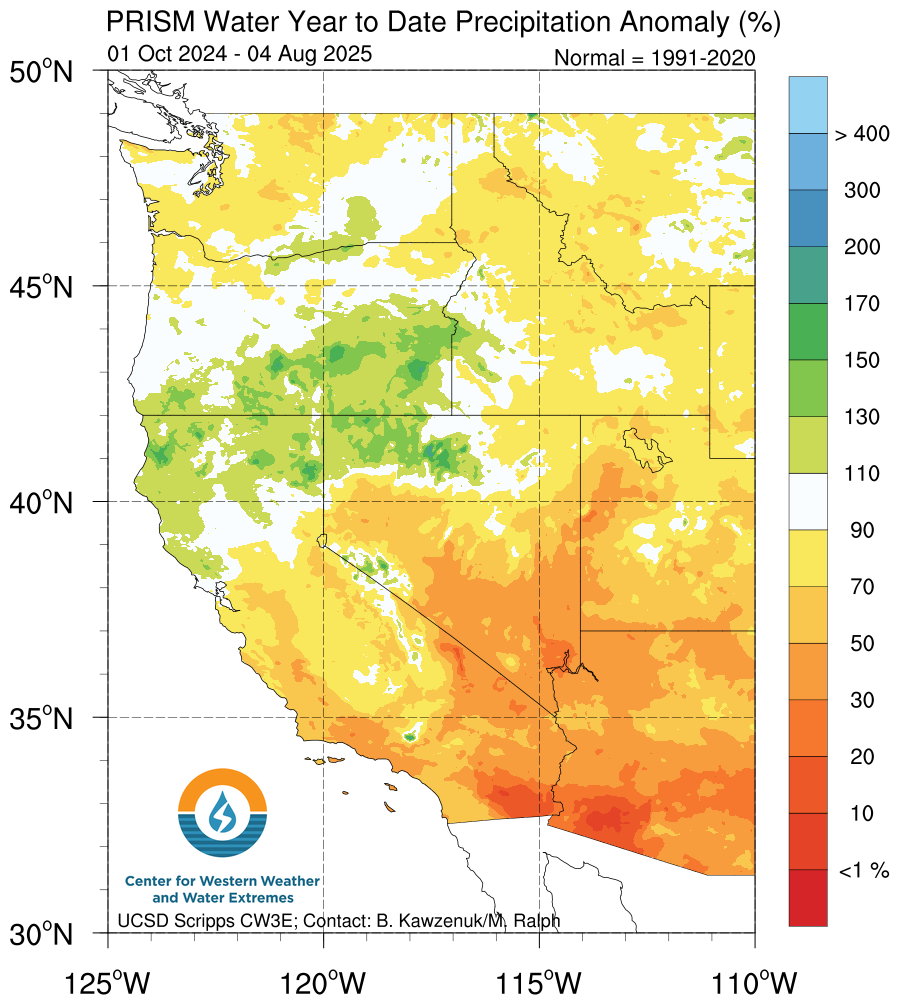
Water year precipitation
Seasonal precipitation

Snow water equivalent
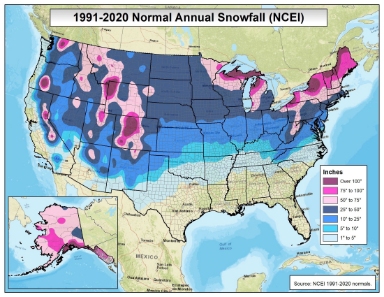
Normal annual snowfall

Precipitation records
Click on this image to see individual weather station records of monthly, annual, and record precipitation.
Statewide precipitation maps
Statewide precipitation maps portray 30-year normal amounts of precipitation across the state (PDF format).


