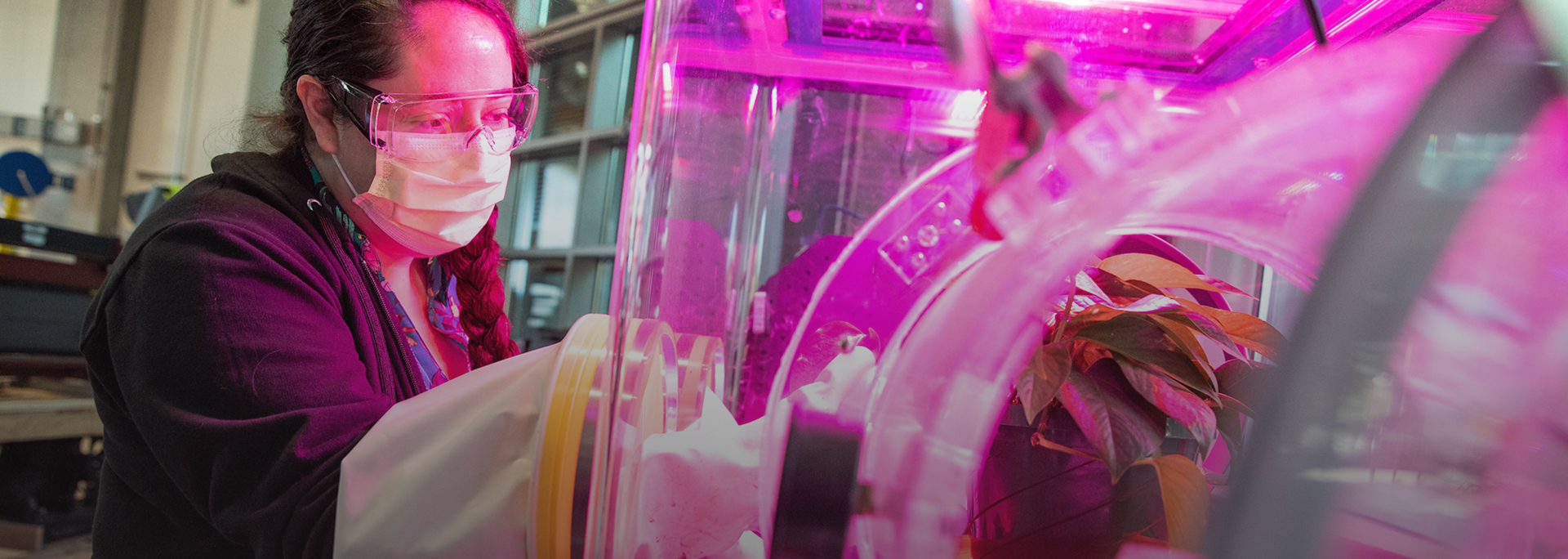

Center for Negative Carbon Emissions
We are advancing technology to capture carbon dioxide directly from ambient air to address environmental degradation, improve air quality and ensure a sustainable, carbon-neutral energy future.
Why carbon capture?
Rising levels of CO2 in our atmosphere and oceans, primarily driven by fossil fuel consumption and deforestation, are directly linked to rising global temperatures, ocean acidification, environmental degradation and a host of socioeconomic challenges. Large-scale carbon removal and storage is key to mitigating past emissions, converting excess carbon into usable products and minimizing future fossil fuel use.
The Center for Negative Carbon Emissions is researching and developing direct air capture technologies to remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. These innovations will help address modern environmental challenges, improve air quality, bring us close to achieving international climate targets and enable a sustainable, carbon-neutral future.

How does carbon capture work?
- Carbon capture works through a series of well-coordinated steps.
- CO2 is extracted from the sorbents into a concentrated stream using heat, vacuum, moisture or other means. The extracted CO2 is purified to meet storage or conversion requirements. For example, using carbon in greenhouses or microalgae ponds to help with growth requires a lower level of purification than storing it underground or creating synthetic fuel.
- CNCE is constantly designing, fabricating and adjusting new capture materials, systems and equipment to test how well these sorbents work and respond to external factors like temperature, humidity, wind speed and environmental contaminants.
- Modeling and computer simulations are used to predict how various factors affect performance along this step chain, and to estimate both the cost and environmental impact of deploying large-scale plants.

How is our approach different?
CNCE is a pioneer in the direct air capture field, developing innovative and comprehensive approaches to removing CO2 and using the captured carbon in productive ways. The center’s holistic, integrated approach brings together leading experts in state-of-the-art materials science, advanced computational modeling and process design to conduct research at various scales, from labs to pilot plants. Our work with carbon brings together experts in carbon storage, carbon removal certificates, carbon conversion, education and community outreach, policy and community benefits planning and analysis that will pave the way for large-scale deployment of carbon capture technologies. These have the potential to remove billions of tons of CO2 from our ecosystems per year, while providing socioeconomic benefits to the people and communities hit hard by fossil fuel plant closures.
ASU’s unique environment fosters transdisciplinary research and entrepreneurial innovation, integrating diverse fields to address complex challenges. By focusing on real-world implications and sustainability, CNCE aligns with ASU’s broader mission to create impactful, transformative solutions for global carbon management.
World-renowned researchers
Matthew Green
Associate Professor and Director
School for Engineering of Matter, Transport and Energy
Green is the Director of the Center for Negative Carbon Emissions. His research focuses on polymers for use in applications such as water purification, carbon dioxide capture, and nanocomposites.
Klaus Lackner
Research Professor
School of Sustainable Engineering and the Built Environment
Lackner developed mineral sequestration, zero emission power plants and direct air capture to balance the carbon budget. He closes the carbon cycle producing fuels and plastics with CO2 from air, water and renewable energy.

Innovative research projects

MissionDAC
Molecular mechanisms of moisture-driven DAC focuses on molecular mechanisms of moisture-driven DAC. The project brings together researchers from Northern Arizona University, Arizona State University and University of Texas at Austin to engage in coordinated, fundamental research on sorbent materials that release captured CO2 using moisture, rather than energy-intensive heat or vacuum pressure. Learn about MissionDAC
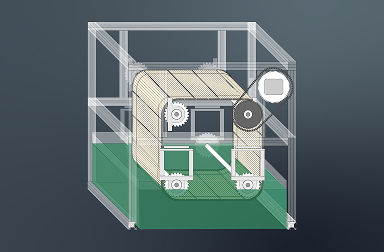
AUDACity
ASU’s DAC polymer-enhanced cyanobacterial bioproductivity project focuses on developing innovative sorbent materials that capture CO2 when dry. The captured carbon is released when the sorbent material comes into contact with cultivation liquids, enhancing the productivity of cyanobacteria.
Partner with us
The Center for Negative Carbon Emissions’ work is made possible through collaboration. Through joint research proposals, service center resources and community outreach efforts, CNCE fosters a sense of community. We work with a variety of other entities and organizations on collaborative research proposals, projects and initiatives. Some of our partnerships include:
- Reacting CO2 with minerals in Arizona
- Arizona Geological Survey
- Northern Arizona University
- Developing clean fuels from captured CO2
- National Renewable Energy Laboratory and Air Company
- Researching moisture-driven direct air capture
- Northern Arizona University
- University of Texas, Austin
CNCE leads the Southwest Regional Direct Air Capture Hub, which brings together DAC technology developers and suppliers, community members and regional stakeholders to design and build a 1 million ton per year CO2 removal process.
Additionally, CNCE engages in outreach and education, developing curricula and fostering community awareness about carbon capture. CNCE seeks to ensure that its technology is accessible and contributes to positive social and economic impacts.
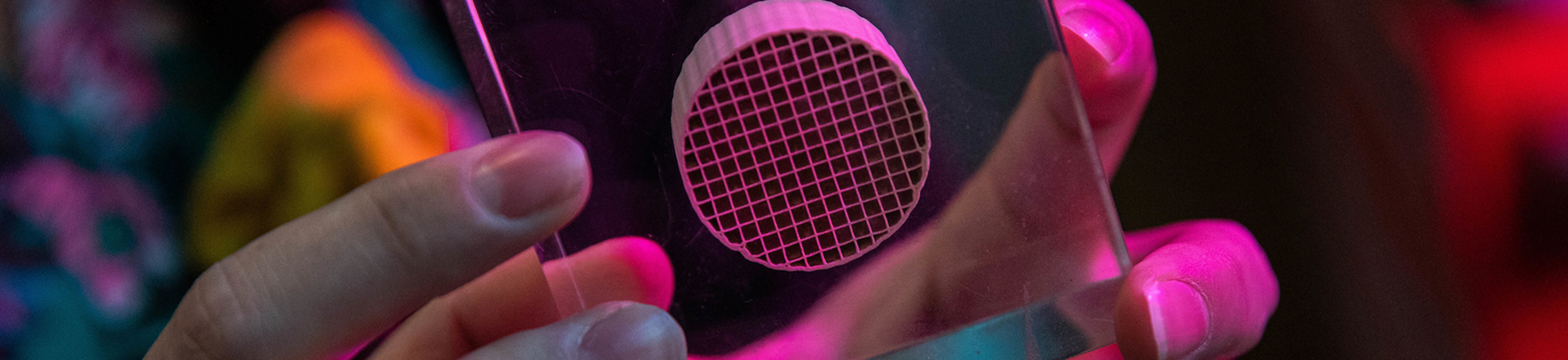
CNCE considers the economic, political, social and environmental benefits of developing accessible air capture technology.
The center’s long-term goal is to become an intellectual leader in this new field of sustainable energy infrastructure design, which is critical to achieving a carbon-negative energy economy.