Summary
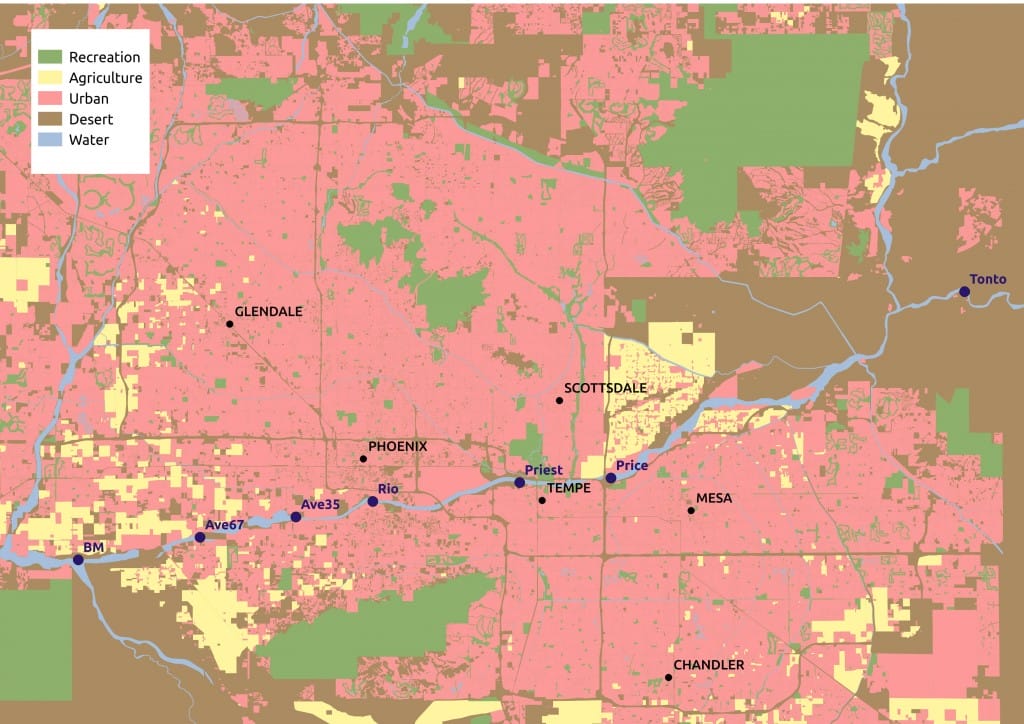
In the southwestern United States, the Salt River has been extensively modified since the early 1900s by upstream dams and diversion canals, resulting in a mostly desiccated river bed throughout most of the greater Phoenix metropolitan area. To restore environmental amenities along the Salt, some portions of the river and its riparian zone have undergone active restoration. Planting vegetation, irrigation, building terraces and garbage removal are among the activities that occur at actively restored areas. At the same time, numerous unintended wetland areas have emerged along the river as a result of urban water source inflows, such as the discharge of municipal effluent, irrigation water or storm runoff. Unlike actively restored areas, the unplanned wetland areas feature only a volunteer flora.
To investigate the capacity of these novel systems to support wildlife and to assess the efficacy of actively restored systems and unintended wetlands, CAP LTER began monitoring birds and herpetofauna (reptiles + amphibians) at select locations along the river in 2012. Monitoring locations focus on reaches of the river with different characteristics, including: urbanized with perennial water and actively restored (n=2 reaches); urbanized with perennial water and passively restored (n=2 reaches); urbanized with ephemeral water but not restored (n=2 reaches) and non-urban reference areas with perennial water (n=1 reach). This program expands on bird monitoring that CAP LTER has been conducting in and around the greater Phoenix metropolitan area, including at numerous riparian sites, since 2000.
Datasets
- Long-term monitoring of herpetofauna along the Salt and Gila Rivers in and near the greater Phoenix metropolitan area, ongoing since 2012
- Point-count bird censusing: long-term monitoring of bird abundance and diversity along the Salt River in the greater Phoenix metropolitan area, ongoing since 2013
- Bird surveys along the Salt River in and near the greater Phoenix metropolitan area: 2012-2013
- Herpetofauna and Riparian Microhabitat of Urban and Wildland Reaches Along the Salt River, Arizona
- Vegetation surveys at CAP LTER riparian-area bird-monitoring locations in the greater Phoenix metropolitan area (2013)
- Seasonal and annual vegetation surveys of wetlands along the Salt River in and near the greater metropolitan area of Phoenix, Arizona
Publications
- Bateman, H. L., J. A. G. Clark, and F. S. de Albuquerque. 2025. Drought and Vegetation Lag Effects Influence Lizard Abundance: A 10-Year Study of Perennial and Intermittent Urban River Areas. Ecohydrology 18(3). DOI: 10.1002/eco.70039.
- Banville, M. J., H. L. Bateman, S. R. Earl and P. S. Warren. 2017. Decadal declines in bird abundance and diversity in urban riparian zones. Landscape and Urban Planning 159(Mar):48-61. DOI: 10.1016/j.landurbplan.2016.09.026.
- Bateman, H. L., J. C. Stromberg, M. J. Banville, E. Makings, B. D. Scott, A. Suchy and D. Wolkis. 2015. Novel water sources restore plant and animal communities along an urban river. Ecohydrology 8(5):792-811. DOI: 10.1002/eco.1560.
- Banville, M. J. and H. L. Bateman. 2012. Urban and wildland herpetofauna communities and riparian microhabitats along the Salt River, Arizona. Urban Ecosystems 15:473-488. DOI: 10.1007/s11252-012-0228-5.